Silent mutations cause a change in the sequence of bases in a DNA molecule but do not result in a change in the amino acid sequence of a protein Figure 1. Frameshift mutation or deletion mutation.

Pin On The Science Duo Products
Match the type of chromosomal mutation with its definition - deletion- loss of a portion of a chromosome.

. Depending on the consequences it has for the body and its offspring we can talk about. A mutation is said to be punctual when it touches one or more nucleotides of the same gene. The effect of a mutation can depend on the region in which the sequence of genetic material has been changed.
Deletions are mutations in which a section of DNA is lost or deleted. Place the types of mutations found in humans in the correct order going from most frequent to least frequent. Thymine is removed Adenine is replaced with thymine and guanine 1.
Match the types of mutations to their definition. They are those that have to do with the shape or appearance of your body once the development stages are completed. The simplest and the most harmless are.
Definition Types and Examples. Morphological mutations have to do with the appearance of the body. Abnormal amino acid sequence5.
It occurs as a result of replacement of one nucleotide by other in specific nucleotide sequence of gene. Point mutation are two types based. Gene mutation where the allele of a.
Single nucleotide substitution Adenine thymine and guanine are. Add or delete 1 or 2 nucleotide letters thereby changing the reading frame for the gene. Frame-shift mutation Guanine is replaced with cytosine 2.
The mutation is a phenomenon in which sudden change in the DNA sequence takes place which results in the change of genotype and ultimately variation in the phenotype. Types of mutation. Mutations occurring in the genes which are somatic or vegetative in this location have been termed somatic mutation.
Since protein-coding DNA is divided into codons three bases long insertions and deletions can alter a gene so that its message is no longer correctly parsed. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. Changes in the flowers fruits stem foliage of a plant are the mutation examples seen in plants.
Depending on the type of cell mutation can be of following types. Small-scale mutations are types of gene mutations such as those affecting a small gene in one or a few nucleotides including. In biology mutations refer to changes in chromosomes and genes which typically manifest physically.
Thus broadly mutation maybe. Answer to Match the type of mutation with its definition the addition or removal of a nucleotide V Choose non functional mutation change in one nucleotide base pair ex SolutionInn Toggle navigation Menu. Match the type of chromosomal mutation with its definition-Deletion---loss of a.
By the replication errors exposure to mutagens and viral infections change or alteration occurs in a DNA sequence that causes genetic abnormalities known as mutation. Mutation and its types Mutation is a process that produces a gene or chromosome that differs from the wild type. A mutation that results in changing a codon such that a different amino acid is specified.
Solutions for Chapter 12 Problem 5AQ. Coloration shape structure etc. When a mutant somatic cell divides the mutation will pass on to the daughter cells resulting in a population of genetically identical cells.
Example of mutations in humans causing disorder are Turner syndrome Klinefelter syndrome Cystic fibrosis Down syndrome Cry du chat syndrome Color blindness and Canavan are some of the example. The types of mutations include. Do not change the amino acid sequence of the gene product the protein Mutations that replace a codon with a different codon resulting in.
Point mutation brings little phenotypic change as compared to frameshift mutation. Match the type of mutation with its definition. A substituted amino acid2.
Insertions are mutations in which extra base pairs are inserted into a new place in the DNA. Gene mutations and chromosomal mutations are two broad categories in which the mutation is classified. Answer to Match the type of mutation with its definition the addition or removal of a nucleotide V Choose point mutation extreme mutation change in one nucleotide bas SolutionInn.
This results in an altered protein product that has a different amino acid sequence than the original. Large section of protein missing4. This type of mutation is a change in one DNA base pair that results in the substitution of one amino acid for another in.
A mutation that changes a codon that specifies an amino acid to a stop codon resulting in premature termination of polypeptide synthesis. Match the type of mutation to its definition1. Please match each type of mutation with its appropriate description.
At the simplest level a mutation is a change or transformation. The somatic mutation occurs in non-reproductive cells somatic cells. The mutation may result due to changes either on the gene or the chromosome itself.
Based on change in genotype and phenotype mutation are of two types. Definition of mutation. This type of mutation happens when a single base in DNA is substituted with another base for example an A becomes a G-Point _____ mutations are changes that alter the structure of the chromosome itself-Chromosomal.
Most of the mutations observed by de Vries in Oenothera lamarkiana were somatic mutations. Start studying Match the terms Mutation. Subsequently the presence of somatic mutation in the endospermic tissue of maize has been demonstrated by Emerson.
Extra section of repeated amino acids3.

The Different Types Of Mutations Video Khan Academy

Substitution Mutation Definition Examples Types Biology Dictionary
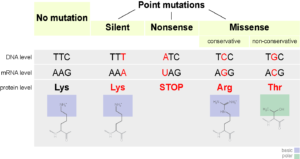
Types Of Mutations Mt Hood Community College Biology 102

Difference Between Gene Mutation And Chromosome Mutation In Tabular Form Chromosome Mutation Biology Lessons

0 Comments